Die Aufgabenstellungen beider Aufgaben wurden in einer Klasse List bzw. Node implementiert, daher wurde auch der Source nur einmal beigelegt. Im folgenden die Lösungen der einzelnen Aufgabenstellungen der Aufgabe 1:
void prepend(Node n) überschreibt den head
der Liste und verweist auf den alten head. viod append(Node n) sucht den letzten Knoten der Liste (in
einer while-Schleife) und setzt in diesem einen Verweis auf den übergebenen
Knoten. boolean sorted() überprüft alle Knoten beginnend
bei head ob deren Werte aufsteigend sind. void insert(Node n) überprüft vor dem Einfügen,
ob die Liste sortiert ist, wenn nicht wird eine NotSortedException
erzeugt. Ist sie sortiert, werden die Werte der Knoten iterativ überprüft,
sobald die entspr. Stelle gefunden ist, wird der Knoten durch Anpassung der
next-Verweise entspr. eingefügt. String toString() durchläuft ebenfalls iterativ alle Knoten
und baut aus den Werten einen entspr. String.Alle Methoden wurden noch mal ausführlich im Source dokumentiert.
/**
* Softwareentwicklung I - Exercise 6/1+2.
* Ordinary chained linear list of nodes (with int values).
* In-source comments are followed by the described code.
*
* @see Node, NotSortedException.
* @author Daniel Brunthaler (0255054)
* @version 1.0
*/
public class List {
private Node head = null; // head of list.
/**
* Creates an empty list.
* @see java.lang.Object#Object()
*/
public List() {
super();
}
/**
* Creates a sorted (ascending values) list with the given values.
* @param values which should be inserted into the new list.
*/
public List(int[] values) {
this();
if (values.length > 0) {
head = new Node(values[0]);
}
for (int i = 1;i < values.length;i++) {
try {
insert(new Node(values[i])); // use insert() method.
} catch (NotSortedException e) {}
}
}
/**
* Prepend the given node.
* @param n node which should be prepended.
*/
public void prepend(Node n) {
if (head == null) { // empty list => first node in list.
head = n;
} else {
n.setNext(head);
head = n;
}
}
/**
* Append the given node.
* @param n node which should be appended.
*/
public void append(Node n) {
n.setNext(null); // last node => no next node.
if (head == null) { // empty list => first node in list.
head = n;
} else {
Node last = head;
while(last.getNext() != null) { // find last node.
last = last.getNext();
}
last.setNext(n); // append given node.
}
}
/**
* Test if values of nodes of list are in ascending order.
* @return true if list is sorted, false if not.
*/
public boolean sorted() {
Node n = head;
while (n != null && n.getNext() != null) {
if (n.getValue() > n.getNext().getValue()) {
return false;
}
n = n.getNext();
}
return true;
}
/**
* Insert given node in the right place of sorted list so that the list
* remains sorted.
* @param n node which should be inserted.
* @throws NotSortedException if list is not sorted
* (boolean sorted() = false).
*/
public void insert(Node n) throws NotSortedException {
if (head == null) { // list is empty.
head = n;
head.setNext(null);
} else if (!sorted()) { // list is not sorted.
throw new NotSortedException();
} else {
Node before = null;
Node after = head;
while (after != null) {
if (n.getValue() < after.getValue()) {
if (before == null) {
// value is smaller than head of list => prepend node.
prepend(n);
} else {
before.setNext(n);
n.setNext(after);
}
return;
}
before = after;
after = after.getNext();
}
// value is bigger than last node of list => append node.
append(n);
}
}
/**
* Returns the list in an adquate String.
* @return a String with all values of the nodes
* of the list seperated by comma.
*/
public String toString() {
String values = "empty";
Node n = head;
if (n != null) {
values = "" + n.getValue();
n = n.getNext();
while (n != null) {
values += ", " + n.getValue();
n = n.getNext();
}
}
return values;
}
/**
* Empty the list.
* Only head is set to null, the garbage collector should do the rest.
*/
public void empty() {
this.head = null;
}
/**
* Invert the list. Means to reverse order, so the last node is the
* head and the head is the last node.
*/
public void invert() {
Node n, before, next;
if (head != null) {
before = head;
n = head.getNext();
head.setNext(null);
while (n != null) {
next = n.getNext(); // remember the next node.
n.setNext(before); // reverse the "node connection".
before = n; // remember the last node.
n = next; // process the remebered next node.
}
head = before;
}
}
/**
* Duplicate the list and all containing nodes.
* @return List which was duplicated from this list.
*/
public List duplicate() {
List list = new List();
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
// append value of node for node of this list
// to the new list in a new Node.
list.append(new Node(n.getValue()));
n = n.getNext();
}
return list;
}
/**
* Merge this list with another list. All nodes of the merging list
* are deleted after inserting into this list. The nodes are inserted so
* that this list remains sorted.
* @param l list which should this list merged with.
* @throws NotSortedException if this or the merging list is not sorted.
*/
public void merge(List l) throws NotSortedException {
if (sorted() && l.sorted()) {
Node n = null;
n = l.head;
while (n != null) {
// "forget" node which was added to this list.
l.head = n.getNext();
insert(n); // insert node in this list.
n = l.head; // process next node.
}
} else {
throw new NotSortedException();
}
}
/**
* Set head of this list to the given node.
* @param n node which should the head of this list set to.
*/
public void setHead(Node n) {
head = n;
}
/**
* Starts a simple command interpreter with possiblity of creating lists
* and testing the certain methods on this lists.
* @param args no arguments have to be given.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String cmd, input, done = "done";
int value, i;
List list = new List();
int values[] = {5,6,7,8,9};
List mergelist = new List(values); // mergelist for testing of merging.
do {
cmd = null;
IO.write("cmd>");
input = IO.readLine(); // read command + argument.
i = input.indexOf(" ");
if (i > 0) {
cmd = input.substring(0,i).trim(); // extract command.
// extract argument.
input = input.substring(i,input.length()).trim();
} else {
cmd = input.trim();
}
try {
if (cmd.equals("prepend")) {
// Prepend given value to the list.
value = Integer.parseInt(input);
list.prepend(new Node(value));
IO.writeLn(list.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("append")) {
// Append given value to the list.
value = Integer.parseInt(input);
list.append(new Node(value));
IO.writeLn(list.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("sorted")) {
// Output if list is sorted.
IO.writeLn(list.sorted());
} else if (cmd.equals("insert")) {
// Insert given value into the list.
// Possible only if list is sorted.
value = Integer.parseInt(input);
try {
list.insert(new Node(value));
IO.writeLn(list.toString());
} catch (NotSortedException e) {
IO.writeLn("list not sorted!");
}
} else if (cmd.equals("invert")) { // Invert the list.
list.invert();
IO.writeLn("inverted list: " + list.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("duplicate")) {
// Duplicate the list and output the new list.
List duplicatedList = list.duplicate();
IO.writeLn("duplicated list: " + duplicatedList.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("merge")) {
// Merge the list with mergelist (see above).
try {
IO.writeLn("mergelist: " + mergelist.toString());
list.merge(mergelist);
IO.writeLn("new list: " + list.toString());
IO.writeLn("mergelist: " + mergelist.toString());
mergelist = new List(values); // create new mergelist
} catch (NotSortedException e) {
IO.writeLn("list not sorted!");
}
} else if (cmd.equals("print")) {
// Print values of the list.
IO.writeLn(list.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("empty")) { // Empty the list.
list.empty();
IO.writeLn(list.toString());
} else if (cmd.equals("quit") | cmd.equals("exit")) {
// Quit the program (see while statement beneath).
} else {
IO.writeLn("unknown command!");
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// Output an error message if given argument is not numeric.
IO.writeLn("value not numeric!");
}
} while (!cmd.equals("quit") & !cmd.equals("exit"));
System.exit(0);
}
}
/**
* Softwareentwicklung I - Exercise 6/1+2.
* Node of a list.
* In-source comments are followed by the described code.
*
* @see List.
* @author Daniel Brunthaler (0255054)
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Node {
private int value; // value in node
private Node next = null; // next node in list
/**
* Create a new node with given int value and the given next node.
* @param v value for this node.
* @param n next node.
*/
public Node(int v, Node n) {
this(v);
this.next = n;
}
/**
* Create a new node with the given int value.
* @param v value for this node.
*/
public Node(int v) {
super();
this.value = v;
}
/**
* Get next node.
* @return Node next node.
*/
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
/**
* Set next node
* @param n next node.
*/
public void setNext(Node n) {
next = n;
}
/**
* Get int value of this node.
* @return int value of this node.
*/
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
}
/**
* Softwareentwicklung I - Exercise 6/1+2.
* Occurs in certain operations of the List object, when the list is not sorted.
* In-source comments are followed by the described code.
*
* @see List.
* @author Daniel Brunthaler (0255054)
* @version 1.0
*/
public class NotSortedException extends Exception {}
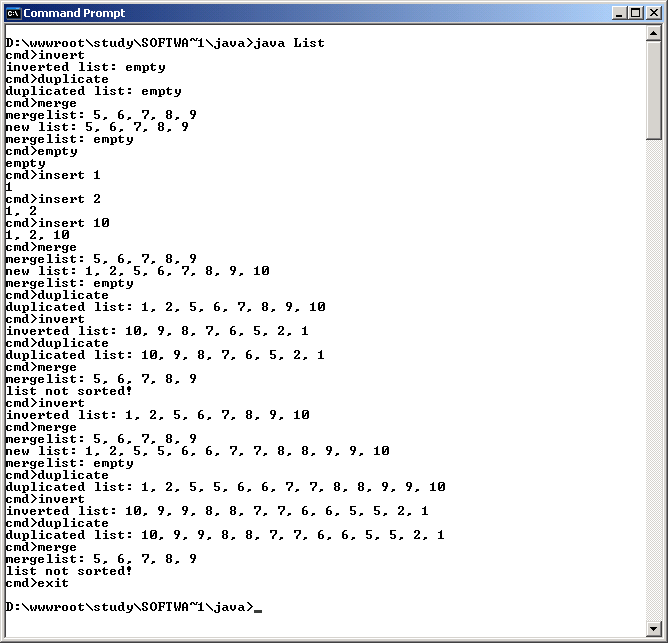
Zum Testen wurde in der Methode List.main(String[] args) ein einfacher
Kommandointerpreter implementiert. Die Kommandos lauten meist gleich wie die
entspr. Methodennamen. Zusätzlich zum Kommando kann, wenn erforderlich,
ein numerisches Argument übergeben werden. In der Klasse List wurde zusätzlich
noch eine Methode void empty() implementiert, welche es ermöglicht,
die Liste zu löschen, wodurch der ges. Test in einem Programmlauf durchgeführt
werden kann.
Folgendes wird getestet:
void insert(Node
n) auf einer unsortierten Listevoid prepend(Node n))void append(Node n))void insert(Node
n)) sowie in eine unsortierte Liste, weiters das Einfügen eines
Wertes, welcher gleich dem Wert eines schon existierenden Knoten der Liste
ist.boolean sorted() auf einer sortierten und einer unsortierten
Liste
Die Aufgabenstellungen beider Aufgaben wurden in einer Klasse List bzw. Node implementiert, daher wurde auch der Source nur einmal beigelegt. Im folgenden die Lösungen der einzelnen Aufgabenstellungen der Aufgabe 2:
void invert() werden die Knoten der Liste iterativ gelesen
und die Verweise auf den nächsten Knoten invertiert, sodass der nächste
Knoten auf den aktuellen Knoten zeigt. Davor muss der nächste Knoten
des nächsten Knoten gemerkt werden, ansonsten würde dieser Verweis
verloren gehen.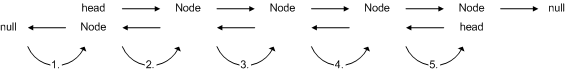
List duplicate() erzeugt eine neue leere Liste, liest iterativ
die Knoten der Liste, erzeugt mit jedem Wert dieser Knoten einen neuen Knoten
und fügt ihn mit void append(Node n) der neuen Liste an.void merge(List l) liest iterativ die Knoten der übergebenen
Liste und fügt diese mit void insert(Node n) in die bestehende
List ein. Durch Setzen von head der übergebenen Liste auf
den nächsten Knoten wird der eingefügte immer wieder entfernt. 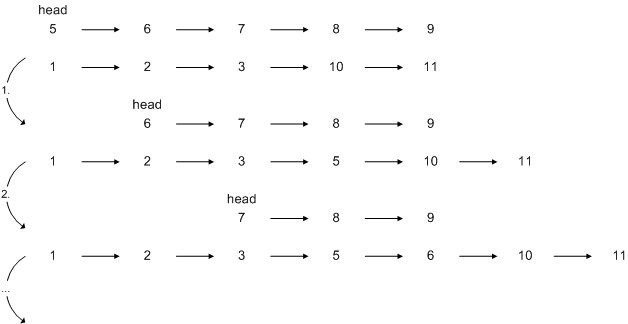
Alle Methoden wurden noch mal ausführlich im Source dokumentiert.
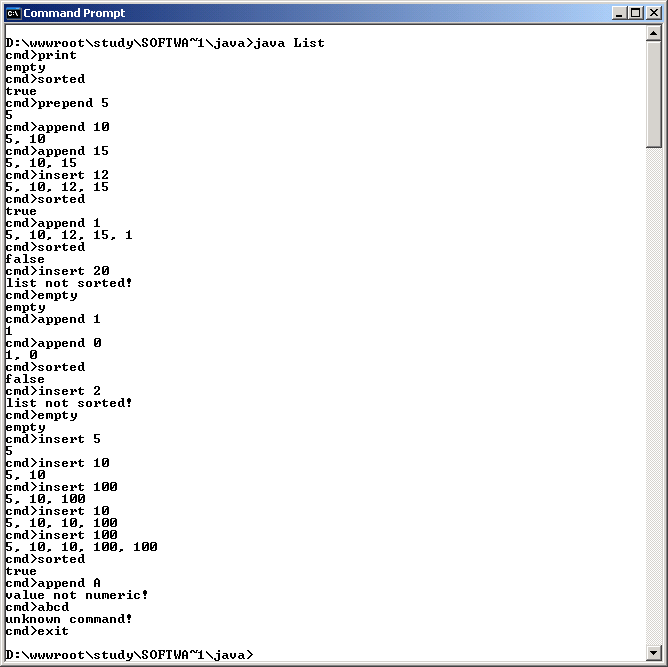
Zum Testen wurde in der Methode List.main(String[] args) ein einfacher
Kommandointerpreter implementiert. Die Kommandos lauten meist gleich wie die
entspr. Methodennamen. Zusätzlich zum Kommando kann, wenn erforderlich,
ein numerisches Argument übergeben werden. In der Klasse List wurde zusätzlich
noch eine Methode void empty() implementiert, welche es ermöglicht,
die Liste zu löschen, wodurch der ges. Test in einem Programmlauf durchgeführt
werden kann.
Folgendes wird getestet:
void invert() auf leerer, sortierter und unsortierter ListeList duplicate() auf leerer, sortierter und unsortierter Liste,
String toString() der duplizierten Liste wird in void main(String[]
args) ausgegebenvoid merge(List l) mit einer hardcodierten Liste {5,6,7,8,9}
(siehe Source void main(String[] args)) auf leerer, sortierter
und unsortierter Liste.